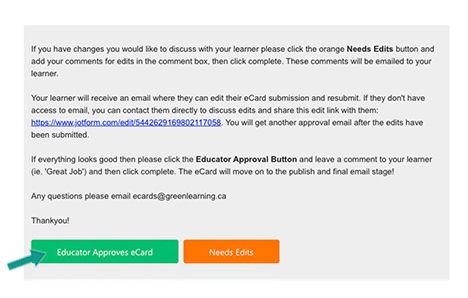
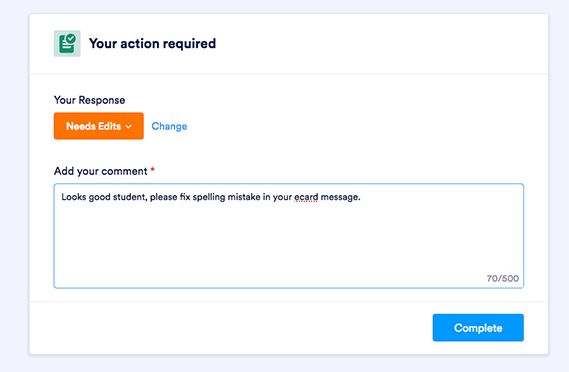
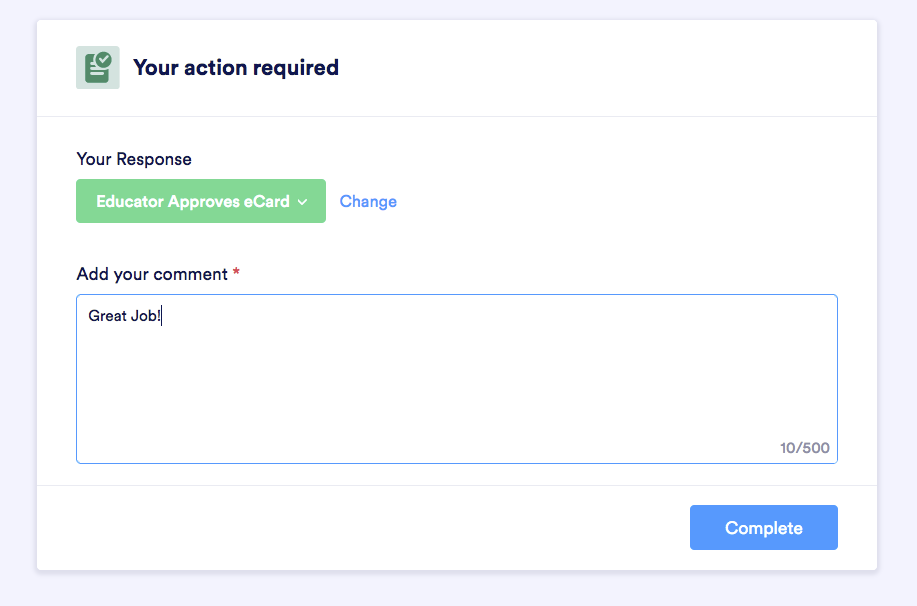
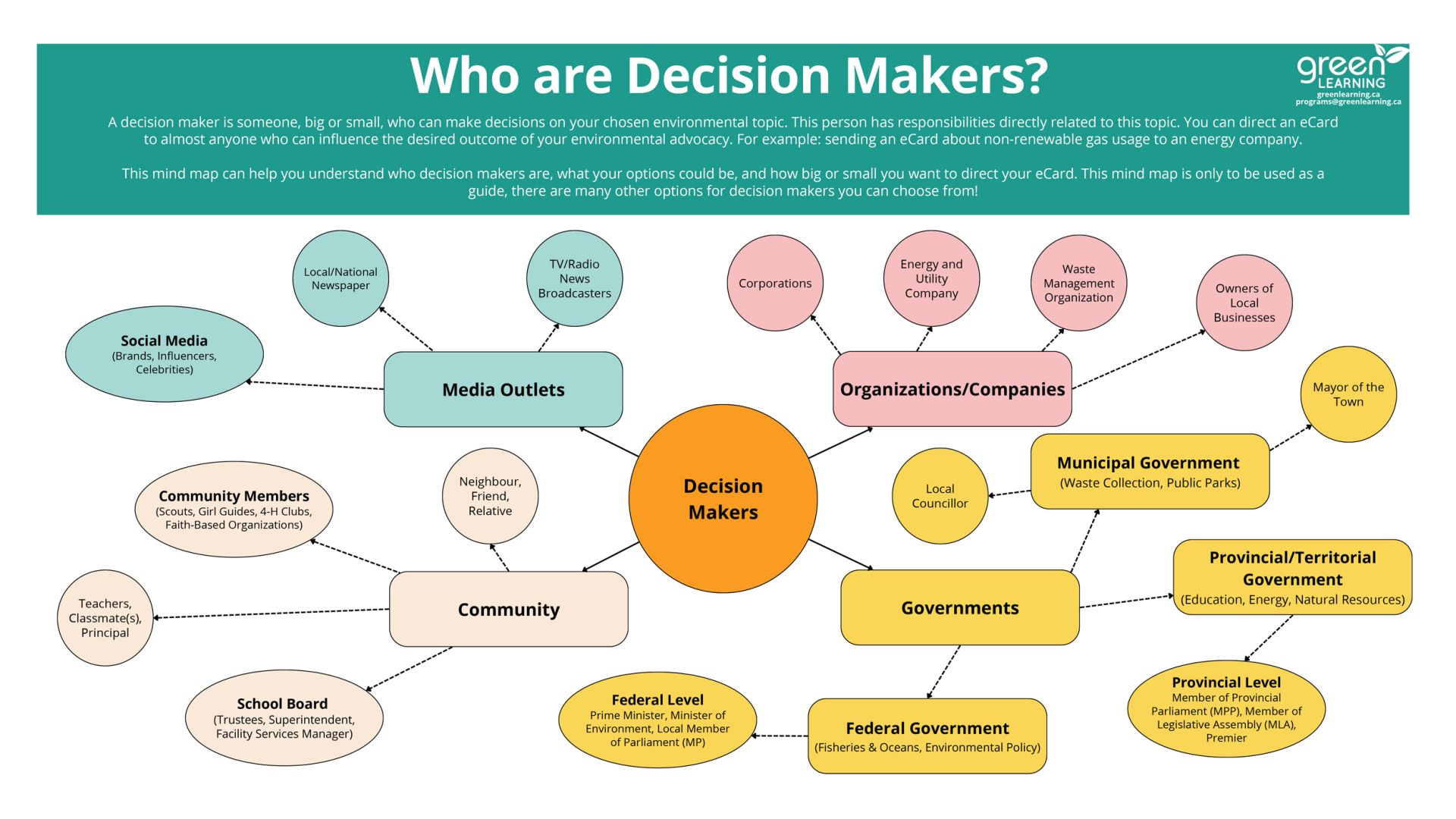
Electrical Energy Calculator - Ontario
This electrical energy calculator was created to support GreenLearning's Energy Revealed Program.
Instructions
To use this calculator, input the watts of the device you are investigating and the minutes a day it is in use. Once you click on 'Calculate Energy' the electricity used (kWh), the greenhouse gases emissions (g of GHGs) produced and cost of electricity ($) will be displayed. Keep scrolling to read more about out what these results mean.
Electricity
(kWh/year)
Results shown here
Environment
(GHG/year)
Results shown here
Cost
($/year)
Results shown here
Kilowatt Hours (kWh)
A watt (W) is the unit used to measure the flow of electrical power. A kilowatt (kW) is 1,000 watts. A kilowatt hour (kWh) is a way to measure the amount of electricity used in an hour.
When you use electricity, the amount of energy consumed is measured in kWhs. The amount of electricity used (kWh) is dependent on how much power your device uses (W or kW) and how long you use it for (Minutes or Hours).
When you use electricity, the amount of energy consumed is measured in kWhs. The amount of electricity used (kWh) is dependent on how much power your device uses (W or kW) and how long you use it for (Minutes or Hours).
kWh Formula
kWh = (watts × hours)
___________
kWh = (watts × hours)
___________
1,000
Greenhouse Gases (GHGs)
GHGs refers to the collection of heat-trapping gases, including water vapour (H20), carbon dioxide (CO2), in our atmosphere. Generating electricity and using energy produces greenhouse gas emissions. Climate scientists agree that the main cause of the current climate crisis is the over-production of greenhouse gases by humans.
Some sources of electricity produce more GHGs than others. For example, burning fossil fuels, such as coal, oil and natural gas produces high amounts of GHGs compared to renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar energy.
Some sources of electricity produce more GHGs than others. For example, burning fossil fuels, such as coal, oil and natural gas produces high amounts of GHGs compared to renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar energy.
Electricity Generation in Ontario
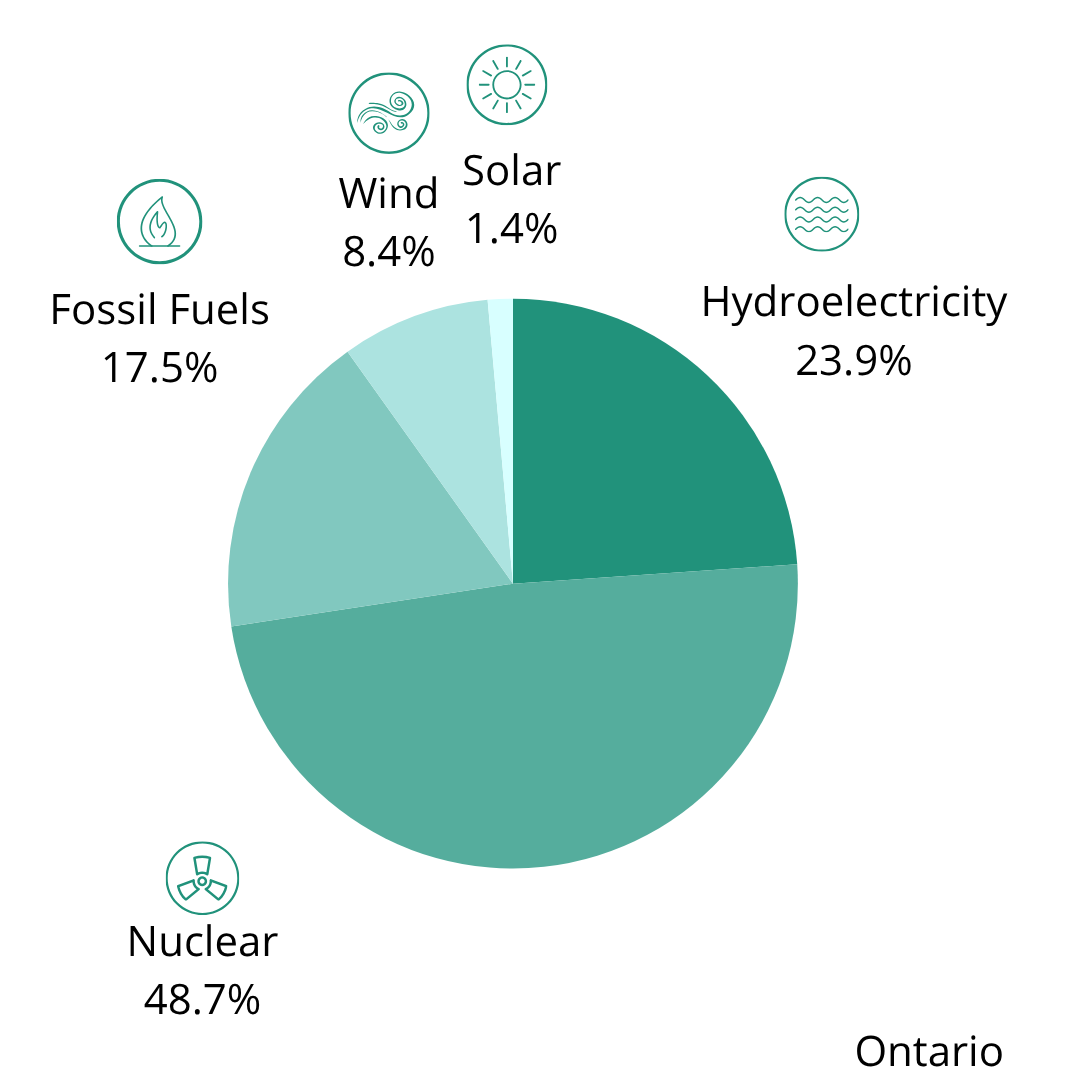
In Ontario, electricity generates on average 35 grams of GHGs per kilowatt hour (35 g/kWh).
Sources
Statistics Canada (2025)
RETScreen Clean Energy Project Analysis Software (2025)
Electricity Rates ($)
Electricity rates are the cost you pay per kWh of energy used. In addition to paying for energy you use, providers will also charge you additional fees. For example, you might pay a delivery fee, which includes costs such as maintaining transmission lines, account management and billing and the energy lost on its way to you.
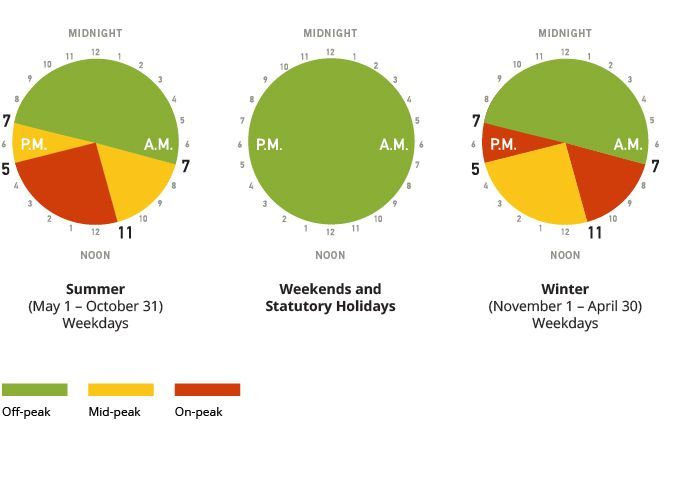
In Ontario, electricity is priced depending on the time of day. This encourages people to change their behaviours in order move their electricity use to off-peak or mid-peaks times. This also helps level the demand for electricity and reduce GHG emissions.
Electricity Rates in Ontario
Off-Peak: 7.60¢/kWh
Mid-Peak: 12.20¢/kWh
On-Peak: 15.80¢/kWh
In Ontario, electricity is priced depending on the time of day. This encourages people to change their behaviours in order move their electricity use to off-peak or mid-peaks times. This also helps level the demand for electricity and reduce GHG emissions.
Electricity Rates in Ontario
Off-Peak: 7.60¢/kWh
Mid-Peak: 12.20¢/kWh
On-Peak: 15.80¢/kWh
Source
GreenLearning
creates free education programs about energy, climate change and green
economy that engage and empower students to create positive change.
Explore
Get Involved
© 2024 GreenLearning. All rights reserved.
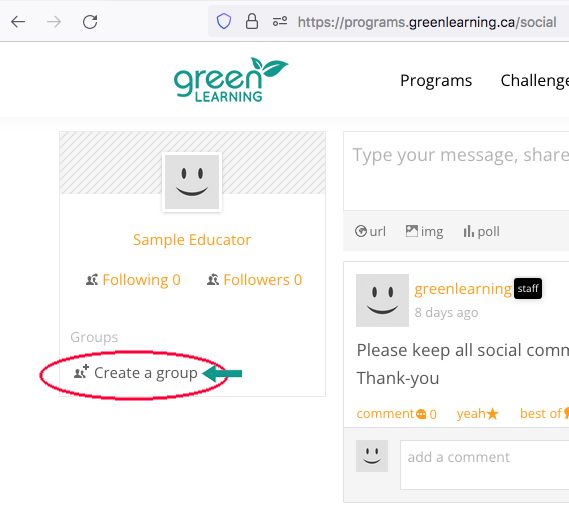
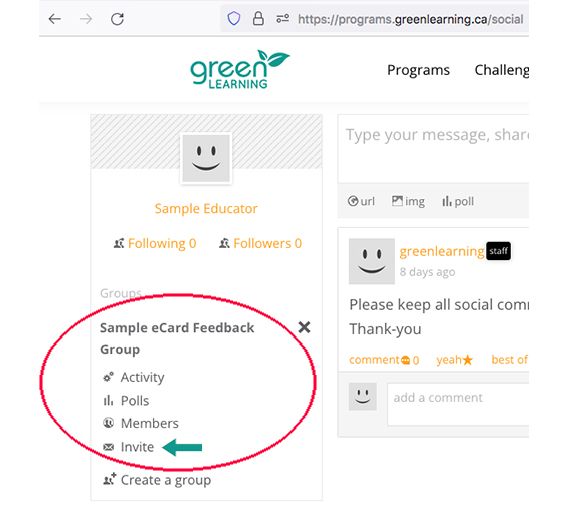
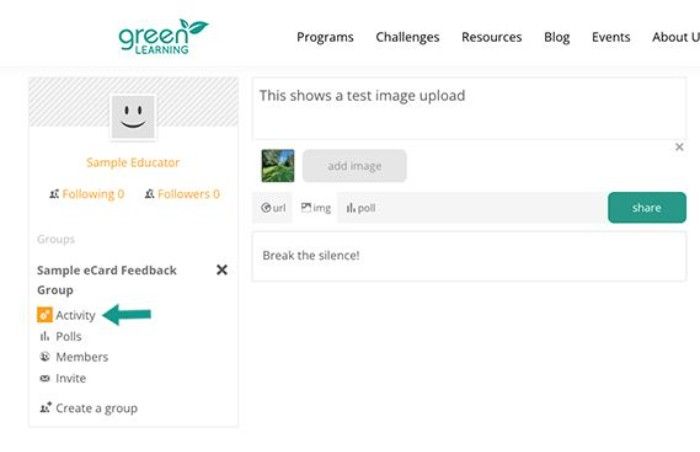
Activity link under private class group.